USER GUIDE 7
Choosing Slicer Settings
An overview of the slicing settings and print parameters that affect 3D print quality.
Object Resolution
Object resolution corresponds to the layer height, which is measured in millimeters or microns.
Smaller layer heights make for higher resolution objects with smooth surfaces. Smaller layer heights will increase print times.
Larger layer heights are considered low resolution, as the print lines are visible.
HIGH
Layer Height: 0.10mm - 0.15mm
Print Time: Long

MEDIUM
Layer Height: 0.16mm - 0.29mm
Print Time: Average

LOW
Layer Height: 0.30mm - 0.40mm
Print Time: Short
Object Infill
The object infill refers to the inside structure and density of a 3D printed object. It is measured in percent.
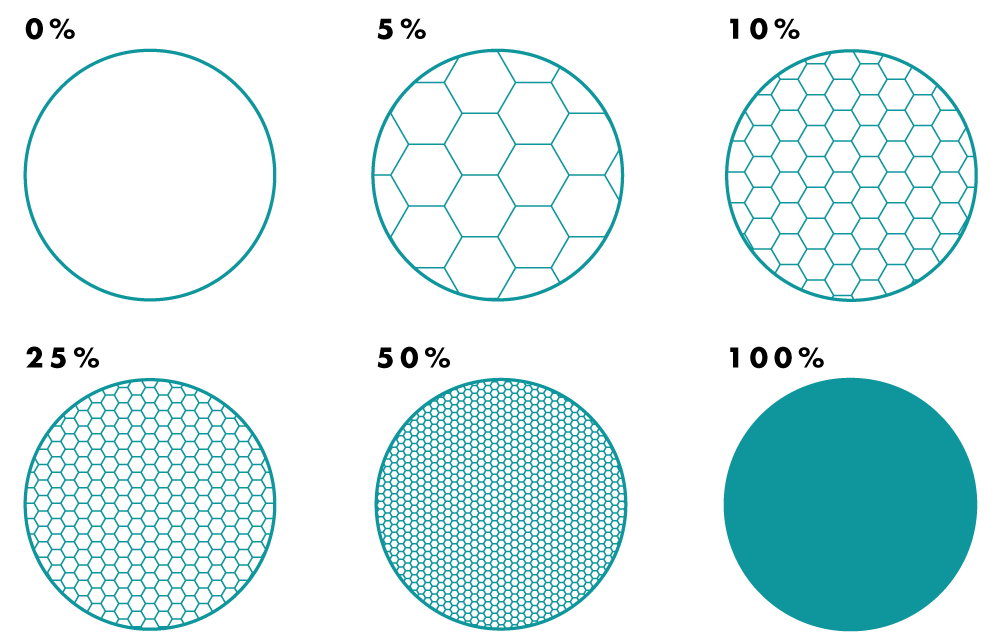 Fig A: Cross-section of cylinders printed with a range of different infills
Fig A: Cross-section of cylinders printed with a range of different infills
Objects that need to stand up under heavy use should have denser infills. The denser the infill, the longer the print time will be. Light use and decorative objects can use less infill to save time and material.
Object Shells
Object shells, or perimeters, are the outer layer(s) of the print that make up the walls of your object. The more shells, the stronger your object will be.
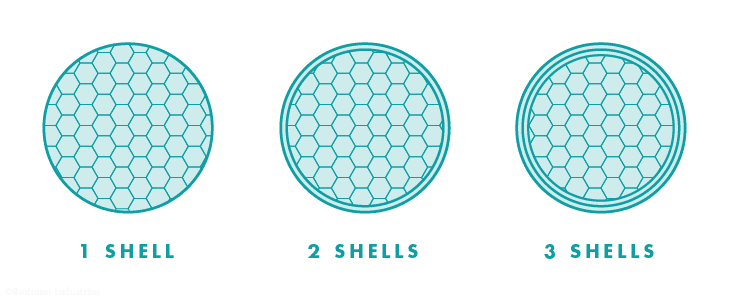 Fig A: Cross-section of cylinders printed with varying shell counts
Fig A: Cross-section of cylinders printed with varying shell counts
Use fewer shells when creating display items, such as sculptures. Use more shells when your 3D printed object needs to withstand heavy pressures or stress, such as mechanical parts. Adding shells will also increase the print time and use more material.
SUPPORTS
Support material is removable and discarded 3D printed material used to successfully fabricate overhangs, bridges, and negative space.
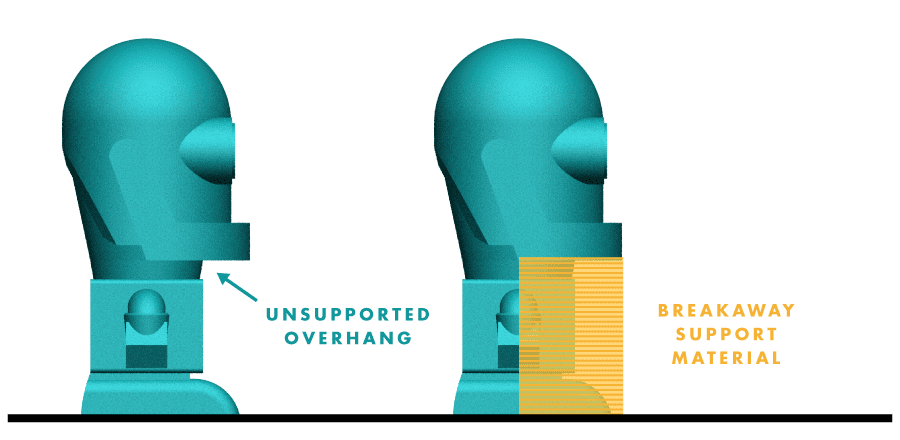 Fig A: Example of when to use support material on an unsupported overhanging feature of a 3D model
Fig A: Example of when to use support material on an unsupported overhanging feature of a 3D model
The image above shows an unsupported overhang at the robot’s chin. Without support material, the chin would sag. Support material ensures successful printing of overhangs by providing a breakaway scaffold.
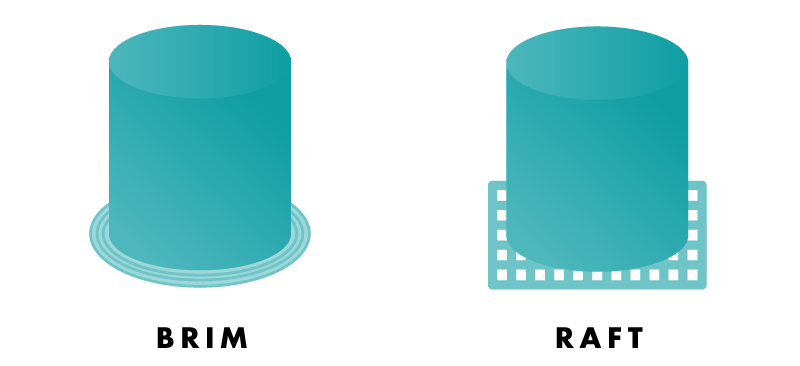
BRIM
Brim is additional material printed around your object to help hold down its edges and prevent warping.
RAFT
Raft is a removable latticework printed underneath an object to help with warping and bed adhesion.
BRIM VS RAFT - WHEN TO USE
While both brims and rafts serve the same purpose, here are key differences:
- A brim uses less material and prints faster but may not provide enough adhesion for small features.
- A raft uses more material and prints slower but provides a stronger foundation for models with small features.
FLAT SIDE DOWN
The position of an object on the build platform can impact print time, accuracy, and strength. Orientate your model so its flat surface is facing down on the build platform.
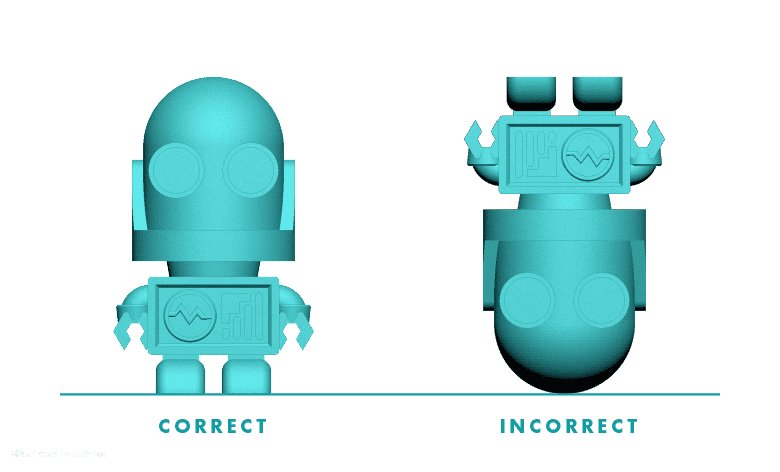 Fig A: Example of how to orient a model for successful 3D printing
Fig A: Example of how to orient a model for successful 3D printing
STRENGTH vs LAYER ORIENTATION
3D printing is done in horizontal layers, building the object from the bottom up. As a rule of thumb, fewer vertical layers make for a stronger object and faster print.
For more detailed instructions on slicing settings, visit Simplify3D® Support Page.
